Do you want to trade safely when markets act hectic? Read this detailed case study so you know exactly how to buy, manage, and sell a stock which means that you will never be confused again what to do next.
Timing Your Entry
Do you ever feel like you’re just guessing when to jump into the stock market? I know I used to. The key is not just to buy low, but to buy at the right moment. Here’s how I do it:
- Watch for Breakouts: I look for stocks breaking out from a stable pattern. This signals strong buying interest.
- Check the Volume: High trading volume confirms that the breakout is real and not just a fluke.
And what about the overall market condition? This brings us to the next crucial step.
Managing Your Investment
Now you’ve bought the stock, but the ride has just begun. Here’s how I keep tabs on my investment:
- Set Alerts: I use price alerts to notify me of significant changes. This way, I don’t have to watch the market every second.
- Stay Updated: I read up on market news and updates related to my stocks daily. Staying informed helps me anticipate changes.
And when do you know it’s time to let go? We’ll get into that next.
Knowing When to Exit
Recognizing when to sell is as important as knowing when to buy. Here’s my strategy for making the exit call:
- Profit Targets and Stop Losses: I set these right after buying. They help automate selling at my desired profit or minimum loss.
- Monitor Market Trends: A sudden downturn in the market might be a signal to sell early.
But what happens after you’ve sold your stock? That’s a question worth exploring.
Post-Sale Strategy
Selling your stock is not the end of the journey. Here’s what I usually do next:
- Review the Trade: I analyze what went well and what didn’t. This helps me improve my strategy.
- Reinvest: With the capital from the sale, I look for new opportunities. The cycle begins anew.
- Set the price alert: When the stock is good but the timing is not, I set the price alert where I want to get back in. This way I won’t miss the next opportunity.
Now, let’s sum up what we’ve covered before we dive into some quick references.
Details at a Glance
- Timing is crucial: Enter at breakouts and high volume.
- Stay vigilant: Set alerts and keep informed about your stocks.
- Exit wisely: Use profit targets and monitor market trends.
- Learn and adapt: Review each trade and plan for the next.
Explanations for the Drawing
The upward purple arrow shows where I bought the stock. The downward purple arrow shows where I sold it.
Green Line 21-day exponential moving average line (see EMA 21 below)
Red Line 50-day simple moving average line (see SMA 50 below)
Black Line 200-day simple moving average line (see SMA 200 below)
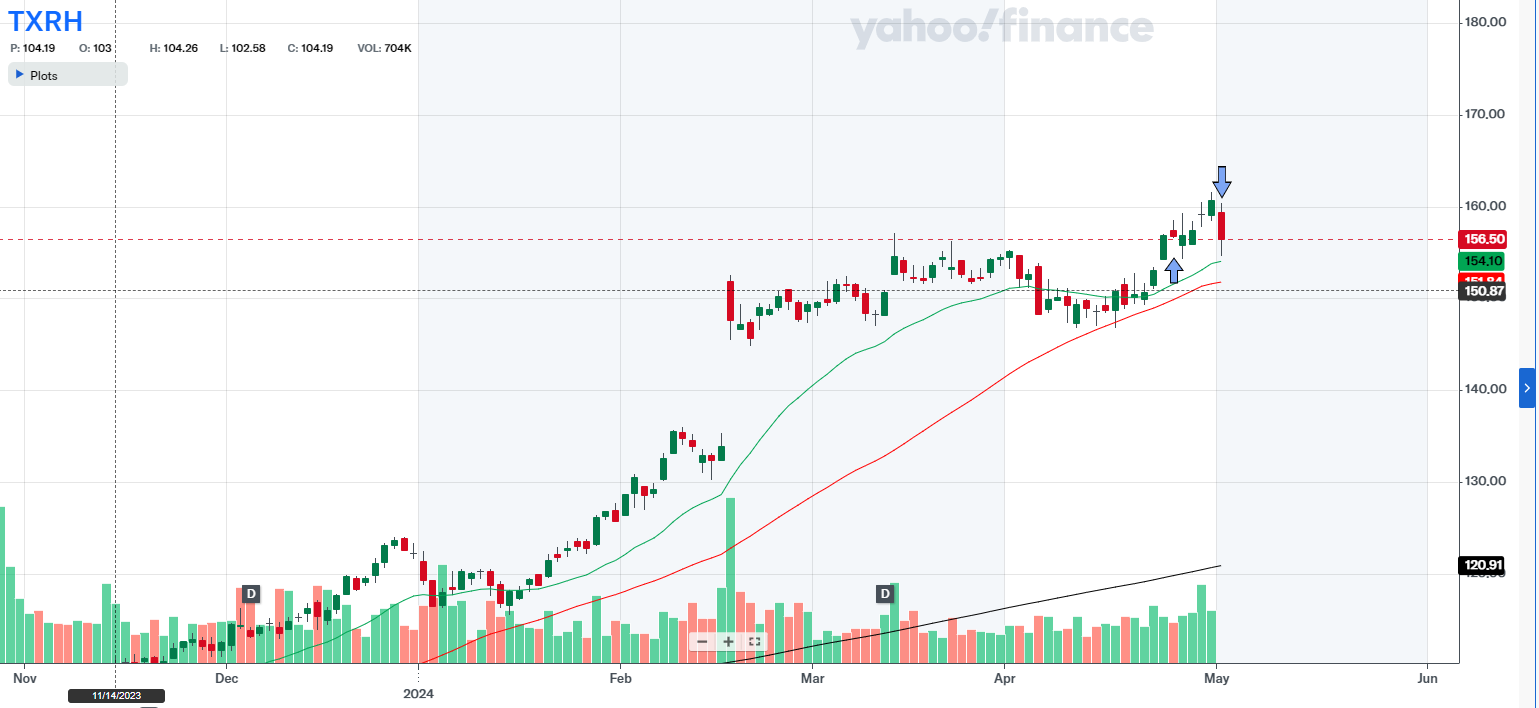
Opening
- Underlying: TXRH
- Date: 24 Apr 2024
- Underlying Price: 157.65
- Stop Loss: 150.30
- Profit Target: 178.00
- Market Outlook: Market in correction
- RS Rating: 93
- RS Line Trend: Upward (U)
- Industry Rank: 5 out of 197
- Volume U/D Ratio: 1.2
- Institutional Ownership Trend: Upward (U)
- Position Risk, %: 4.63
- Position Risk to NL, %: 0.33
- Potential Profit (Position), %: 12.83
- Risk to Reward Ratio: 0.36
- Position Size, %: 7.18
- Reason for Opening Trade:
- Stock was breaking out of a flat base.
- Strong fundamentals.
- Strong price movement since market was in correction.
- Was it an Ideal Buy? No. Volume wasn’t high enough.
- Remarks on Trade Setup:
- I set the stop-loss as close to the buying point as possible, since the market is volatile – slightly below EMA-21.
- Overall price action has been quite steady, which is a strong sign.
- Strength is also indicated by accumulation of the stock.
Closing
- Closing Date: 1 May 2024
- Closing Price: 154.75
- Market Outlook at Closing: Exposure 20-40%
- Did You Place an Alarm to the Stock After Closing? Yes, at 157.12
- RS Rating at Closing: 93
- RS Change at Closing: 0
- Closing Remarks:
- Strong down day. Price sank out of the buy zone. Earnings coming up. Too risky to own right now.
- Since previous price bases have been quite low (which indicates accumulation), it would probably be a good idea to buy the stock back after earnings have been released. Right now I had to sell it because there was no profit cushion built in before earnings release.
Results
- What Went Well:
- I bought when the price just had broken out of the base and was in the buy zone.
- I decisively sold when I saw an abnormal price action downward – I didn’t stand and wait for the stop-loss order to activate. This means that my losses were smaller.
- Cause of Error/Improvement:
- It was a quite risky trade since the earnings release date was close when I opened it.
- Lessons Learned:
- When I buy a stock and have owned it only for a few days and it already has a strong negative price action, I quickly start feeling anxious and start thinking about selling it.
- Position ROI, %: -3.09
- Position ROI (Portfolio), %: -0.22
- Position Open Time (Trading Days): 6
- Position Open Time (Days): 7
And just before we wrap up, let’s clarify some terms you might have come across.
Terms and Definitions
- Breakout: When a stock moves outside a defined price range.
- Volume: The total number of shares traded in a given time period.
- Stop Loss: A set price at which a stock is automatically sold to prevent further losses.
- EMA 21 Calculates the 21-period exponential moving average, highlighting short-term trends.
- SMA 50 Averages the price over 50 periods, showing medium-term trends without overemphasizing recent data.
- SMA 200 Averages the price over 200 periods, revealing long-term trends by treating all data equally.
- Industry Rank Investor’s Business Daily’s system that ranks industries 1 to 197 based on performance. It guides us in CAN SLIM TRADING towards leading sectors.
- U/D Ratio Measures stocks closing up versus down. A ratio above 1.0 indicates bullish sentiment, important in CAN SLIM TRADING.
- RS Rating Ranks a stock’s performance on a 1 to 99 scale. I look for at least 85, showing strong momentum and growth potential.
- RS Line Compares stock price to the market, plotted as a ratio. We seek an uptrend, indicating outperformance and strong momentum.
- Volatility Measures how much a security’s price fluctuates over time. High volatility means large price changes, indicating risk and potential reward.
- Institutional Ownership Trend indicates whether the stock is under accumulation or distribution by the institutions.
- EPS (Earnings Per Share): A financial metric calculated by dividing a company’s net profit by the number of its outstanding shares. It indicates the amount of profit attributed to each share of stock, serving as a key indicator of a company’s profitability.
- Overhead Supply: is a stock market term for a large amount of unsold shares at a certain price level, acting as resistance that prevents the price from rising. It occurs when investors looking to sell at break-even points add to the supply, making it hard for the stock to increase in value until this excess is bought up.
Conclusion
Are you ready to trade like a pro, even when the market throws a curveball? Use these strategies to stay one step ahead of the chaos. Remember, it’s not just about surviving the storm—it’s about thriving in it. So, grab your trading gear and let’s dive into the market whirlwind with confidence!
Next time the market starts bucking like a rodeo bull, just smile and remember: you’ve got the best riding strategy in town!
By the way, if you have any questions or want stock trading tips and advice, feel free to fill out the form here and I’ll get back to you.


